Chainbase (C) is described as the world’s largest hyperdata network, designed to integrate all blockchain data into a unified ecosystem, providing an open and transparent data interoperability layer for the AI era. This platform, with its innovative dual-chain technology architecture, creates an ecosystem that ensures high throughput, low latency, and enhanced cybersecurity. Chainbase’s core mission is to make data accessible and useful, enabling users to fully benefit from the open internet era. So, what is Chainbase (C), and what does it do? Let’s explore it in detail.
What is Chainbase?
Chainbase is an omnichain data network that integrates blockchain data and provides an optimized infrastructure for AI applications. Its dual-chain architecture supports data programmability and composability while delivering high performance, low latency, and a secure environment. The C token serves as the cornerstone of this ecosystem, used to facilitate network operations, governance, and incentivize participants. The platform accelerates the development of Web3 applications by making data access easier for developers and users.

What Problems Does Chainbase Solve?
Blockchain technology offers transparent and immutable data, but issues like data fragmentation and lack of standardization across networks make it challenging to utilize data, especially for AI applications. Chainbase addresses these problems with innovative solutions:
Data Fragmentation and Interoperability
Integrating data across different blockchain networks is a complex process. Chainbase solves this by consolidating all blockchain data into a single platform, providing developers with seamless access.
Centralization Issues
Traditional blockchain data solutions often rely on centralized authorities or single points of failure. Chainbase offers a fully decentralized network, enhancing data transparency and reliability.
Data Processing and Scalability
Large-scale data processing and AI model training are inefficient on traditional blockchain networks. Chainbase’s dual-chain architecture and Manuscript protocol optimize these processes, delivering high performance.
Lack of Incentives for Data Providers
In existing systems, data providers are often under-rewarded. Chainbase incentivizes contributors with the C token, promoting high-quality data production.
Key Features of Chainbase
Chainbase stands out with its innovative technologies and user-centric approach. Here are the platform’s key features:
1. Dual-Chain Architecture
Chainbase’s dual-chain technology combines execution and consensus layers to optimize data processing. This structure ensures high throughput, low latency, and enhanced security. The dual-staking model further strengthens network reliability.
2. Manuscript Protocol
The Manuscript protocol is a programmable framework that transforms raw blockchain data into standardized, AI-compatible formats. It simplifies data creation with general-purpose languages like SQL, offering developers flexibility.
3. Theia and TheiaChat
Theia is Chainbase’s first AI model developed for the crypto world. TheiaChat provides a user-friendly interface for this model, enabling access to blockchain data through natural language. Users can query data and perform trend analysis without technical expertise.
4. Dual-Staking Security Model
Chainbase employs a dual-staking model combining C token and ETH staking. This system enhances network security for operators and validators, while a veto mechanism provides an additional layer of protection against faulty transactions.
5. Multi-Chain Infrastructure
Chainbase supports multiple blockchain networks, including Ethereum, Polygon, BSC, Fantom, Arbitrum. In the future, it plans to offer omnichain strategies covering all blockchain networks.
Use Cases of Chainbase
Chainbase offers a wide range of applications across various sectors and user groups. Here are some examples:
Wallet Management
Users can manage assets across multiple blockchain networks through a single interface, improving ease of use.
Security
Chainbase monitors network attacks, provides security alerts, and conducts in-depth analysis to protect blockchain networks.
Artificial Intelligence
It enhances the accuracy and decentralization of AI models by utilizing data from multiple blockchains.
DeFi
Chainbase supports lending and borrowing across different blockchain networks, increasing liquidity and flexibility in the DeFi ecosystem.
Social Platforms
It enables the creation of social platforms where users from different blockchain networks can share content and interact seamlessly.
Infrastructure
Chainbase provides developers with a robust infrastructure for building innovative applications that utilize data from multiple blockchains.
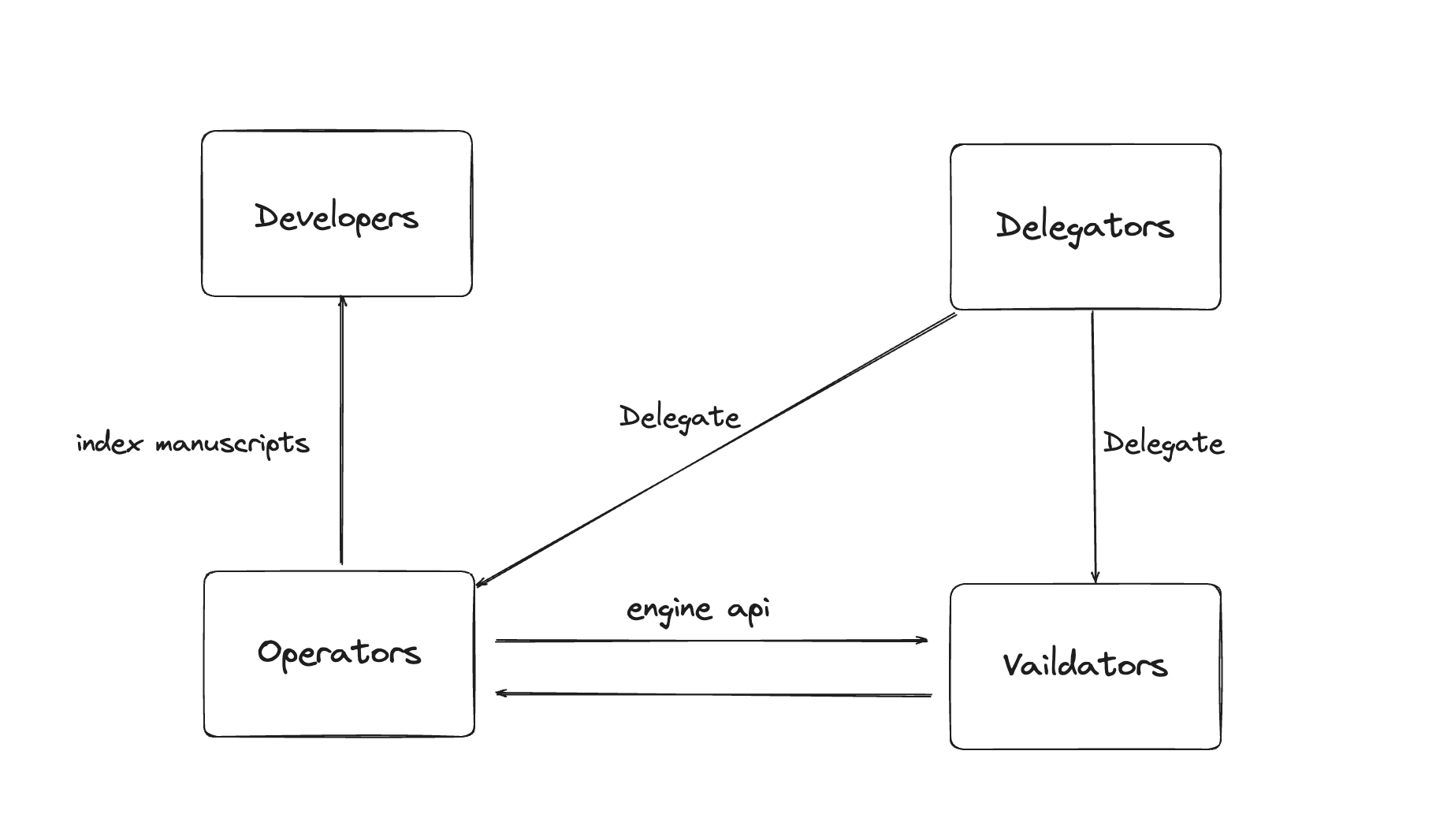
How Chainbase Works
The Chainbase network operates through various roles, each contributing to the ecosystem’s sustainability:
Developers
Developers act as both data providers and users, creating data transformation codes (Manuscripts) using the Chainbase SDK. They develop Manuscripts locally, test them in a sandbox environment, and publish them to the network, earning rewards based on their usage.
Operators
Operators provide computational resources for the network’s execution layer, handling data processing tasks. They can register on the Holesky testnet or Eigenlayer mainnet to become operators. Rewards depend on the quality and quantity of services provided.
Validators
Validators ensure network security and consensus by verifying transactions, maintaining data integrity, and ensuring stability. Becoming a validator requires meeting specific hardware and software requirements.
Delegators
Delegators enhance network security by staking C tokens or ETH to support validators and operators. They earn a share of the rewards generated by the validators and operators they back.
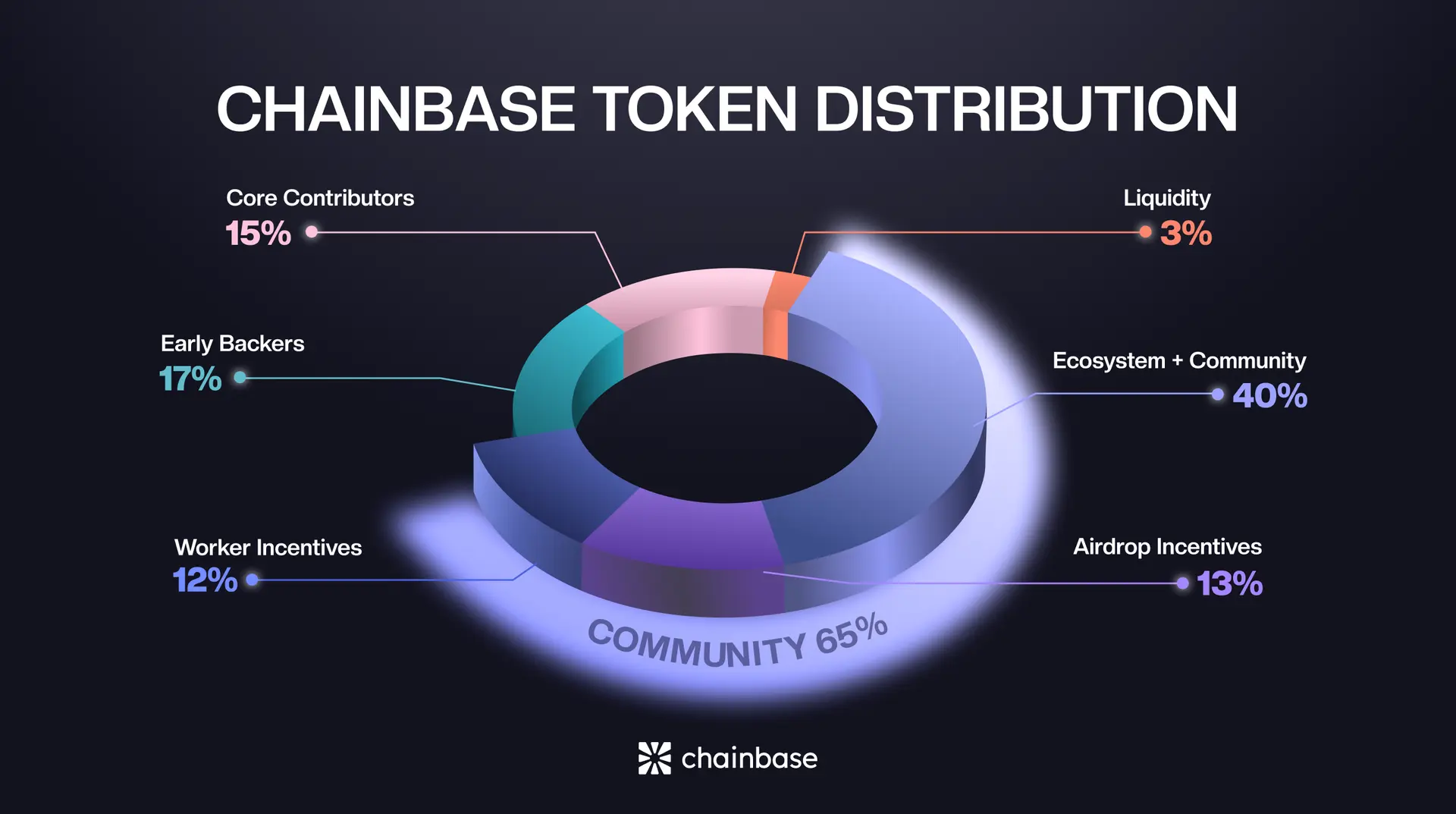
Chainbase (C) Tokenomics
Chainbase has allocated 65% of the total $C supply to ecosystem growth, contributor rewards, and user incentives. This reflects Chainbase’s commitment to open participation and long-term alignment.
- Ecosystem + community: 40%
- Early backers: 17%
- Core contributors: 15%
- Airdrop incentives: 13%
- Worker incentives: 12%
- Liquidity: 3%
Economic Sustainability
-
Inflation Control: Annual token issuance is capped at 3%.
-
Usage Demand: C tokens are required for data queries, staking, and governance, ensuring continuous demand.
-
Performance Incentives: High-performing operators and validators receive greater rewards.
Chainbase Roadmap
Chainbase is advancing with a vision to create an open and decentralized data network. Its roadmap consists of two main phases:
ZIRCON (Genesis)
-
Date: May 27, 2024
-
Objective: Lay the foundation for a secure and decentralized data network.
-
Achievements: Omnichain data standards, decentralized network, developer community economy, crypto world model (Theia), and user empowerment.
Aquamarine
-
Date: March 20, 2025
-
Objective: Expand the Web3 data ecosystem and strengthen AI integration.
-
Goals:
-
Launch of Chainbase Network Explorer
-
Transformation of Manuscripts into an AI-compatible tech stack
-
Token delegation on testnet
-
Development of Data Zones
-
Establishment of a decentralized data access layer
-
Creation of an AI tooling kit
-
Development of specialized AI agents for vertical applications
-
Mainnet launch
-
Chainbase Investors and Backers
Chainbase is supported by leading investors such as Tencent, Matrix Partners, Mask Network, Folius Ventures, Hash Global, Jsquare, and BODL.
Chainbase Founding Team
-
Mogu: Founder and CEO
-
Chris Feng: Founder and COO
-
Masafumi Shimizu: Founder
-
Yuxing Liao: Chief Product Officer (CPO)
-
Tianyang Lai: Chief Growth Officer (CGO)
-
Luki Song: Head of Ecosystem and Strategy
-
Kevin L.: Head of Business Development
Official Links
Also, you can freely share your thoughts and comments about the topic in the comment section. Additionally, please follow us on our Telegram, YouTube and Twitter channels for the latest news and updates.


