Enso (ENSO) is a decentralized shared network designed to generate executable bytecode for smart contracts across various blockchains, rollups, and appchains. Operating as a Tendermint-based Layer-1 blockchain, Enso maps all smart contract interactions, enabling developers to interact with any smart contract on any chain through a single interface. By addressing fragmentation and usability challenges in the blockchain ecosystem, Project empowers developers to create seamless, composable, and unstoppable applications with minimal friction. Let’s explore what Enso is, how it functions, and its potential.
What is Enso (ENSO)?
Enso tackles the complexity and fragmentation of the blockchain ecosystem to deliver a developer-friendly experience. From Bitcoin’s simple shared state, the blockchain space has evolved into a complex landscape with Ethereum’s smart contracts, Layer-1 chains like Solana, Near, and Avalanche, Layer-2 solutions, and app-specific chains (appchains). This diversity creates hurdles for developers, requiring custom adapters, deep understanding of each chain’s nuances, and ongoing integration maintenance. Project resolves this by allowing developers to specify their desired outcome (intent), with network participants generating the necessary bytecode. The project’s token powers gas, governance, and participation incentives, with a total supply of 100,000,000.
Purpose of Enso
Enso aims to enhance blockchain usability by eliminating the complexities of cross-chain smart contract integration. Fragmentation forces developers to navigate multiple chains, understand intricate contract details, and build numerous adapters, leading to resource waste and stifled innovation. Enso enables developers to define their intent—such as a token swap or NFT mint—and offloads the technical execution to the network. This fosters cross-chain composability, prevents vendor lock-in, and accelerates the development of innovative applications.
How Does Enso Work?
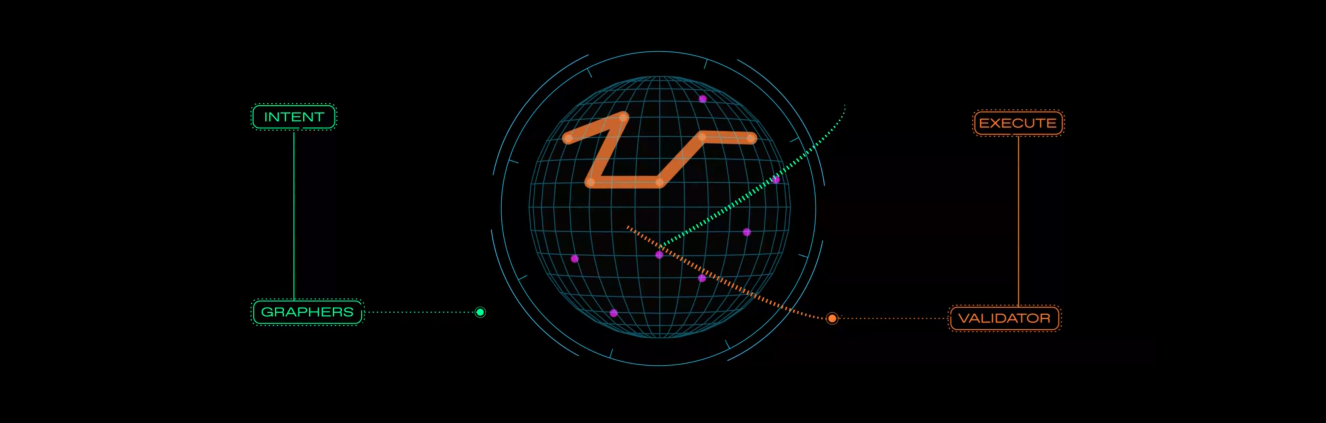
Enso serves as a coordination layer, allowing developers to express intents and receive cross-chain smart contract bytecode. The network operates with four key participants and three core components:
Participants
-
Action Providers: Developers contribute smart contract abstractions (e.g., function signatures, input/output tokens, prerequisites) and earn consumption fees. Contributions are prioritized based on staked Enso tokens.
-
Graphers: Develop algorithms to find optimal solutions, combining abstractions using methods like K-shortest path to produce bytecode. The best solution is selected based on high output and low cost.
-
Validators: Verify requests, validate abstractions, and simulate solutions using ViewFunctions to ensure accuracy, selecting the winning solution.
-
Consumers: Submit intents to request solutions, optionally paying fees.
Core Components
-
Requesting: Developers define their desired outcome as an intent, specifying variables like {IntentId, From, To, Data, Value, AmountOut, Gas}.
-
Abstraction Contribution: Action Providers submit abstractions via messages like MsgAddDeposit, which are parsed into Action types and validated with ViewFunctions. A 9-step validation process ensures integrity before storage.
-
Solution Aggregation: Graphers scan abstractions to generate optimal bytecode, linked to an IntentID. Validators simulate solutions on a chain fork, verify outcomes with ViewFunctions, and select the best solution (highest output, lowest cost). Non-winning solutions are discarded to reduce network bloat.
Fee Mechanism
Solutions may generate fees on target chains. Project conducts a token-based auction, where addresses bid Enso tokens to claim these fees. The tokens are distributed to participants based on their contributions (abstraction usage, solution generation, validation), creating a circular economy.
Roadmap
-
Phase 1: Centralized simulation and Enso-hosted contribution service.
-
Phase 2: Permissionless contributions and broader Grapher participation.
-
Phase 3: Expansion to support EVM, SVM, and MVM ecosystems.
Enso Use Cases
Project provides value in the following areas:
-
Cross-Chain Integration: Seamless interaction with smart contracts across chains.
-
DeFi and NFT Applications: Simplifying complex operations.
-
Gaming and AI Bots: Intent-based execution boundaries.
-
Data Marketplaces: Smart contract-driven data curation.
Usage Steps:
-
Submit an intent request to the Enso network.
-
Contribute as an Action Provider or Grapher.
-
Integrate the resulting bytecode solution.
Advantages of Enso
-
User-Friendly: Abstracts complex integrations.
-
Composability: Enables cross-chain interoperability.
-
Security: Validator and simulation-based verification.
-
Scalability: Supports multiple chains and virtual machines.
Risks of Enso
-
Abstraction Quality: Accuracy of contributed abstractions.
-
Algorithm Efficiency: Performance of Grapher solutions.
-
Chain Compatibility: Potential integration errors.
-
Regulation: Smart contract data usage compliance.
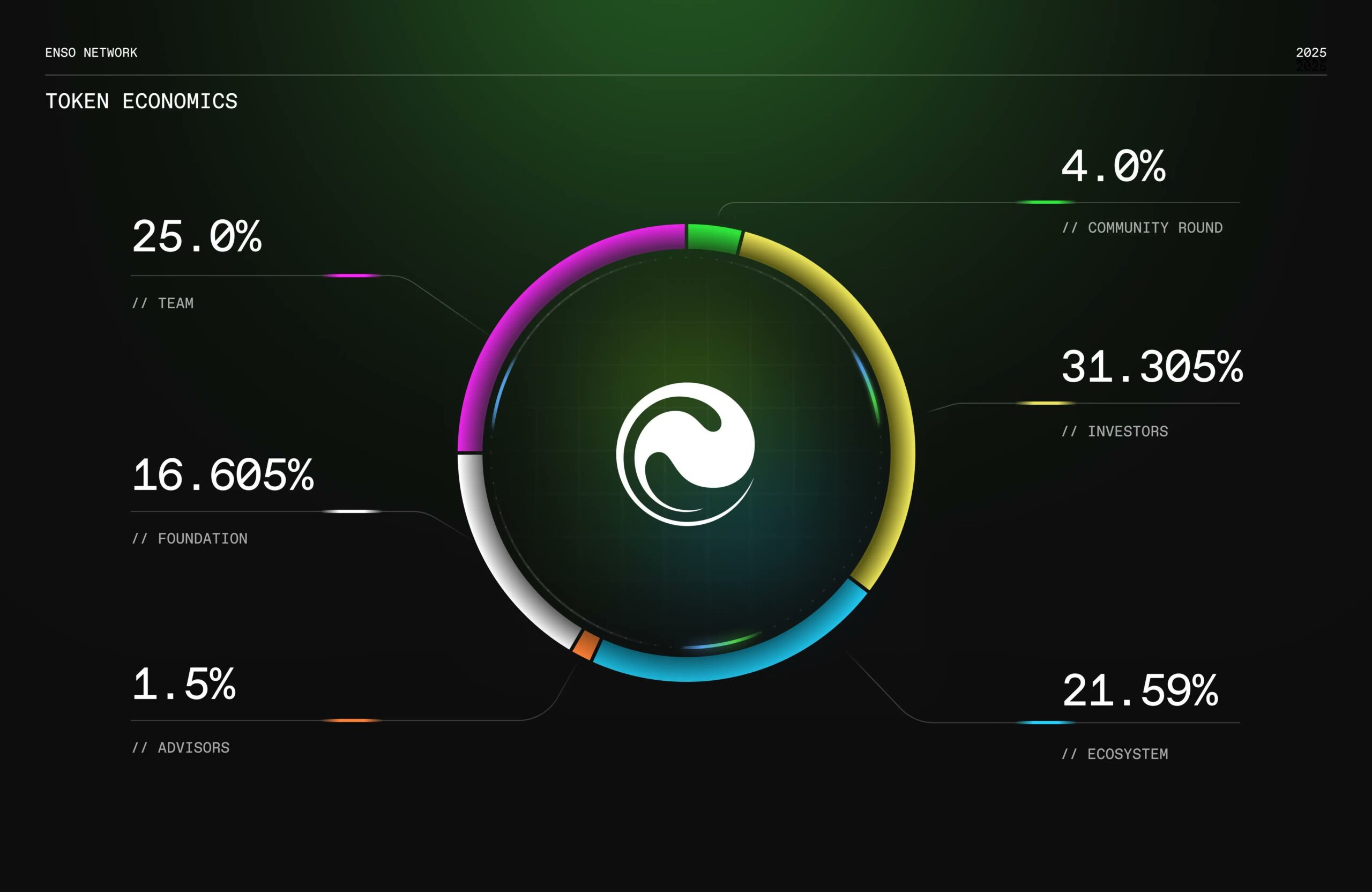
Enso Tokenomics
The Enso token facilitates gas, governance, staking, and delegation; total supply is 100,000,000.
-
Allocation:
-
Team: 25%
-
Foundation: 16.605%
-
Advisors: 1.5%
-
Community Round: 4%
-
Investors: 31.305%
-
Ecosystem: 21.59%
-
Token Utilities:
-
Gas: Powers requests and state changes.
-
Governance: Voting for protocol upgrades.
-
Staking: Participants stake to deter malpractice.
-
Delegation: Enhances network security.
Enso Investors
Project raised $9.2 million from:
-
Tier 1: Polychain Capital, The Spartan Group, Multicoin Capital.
-
Tier 2: Hypersphere Ventures, The LAO, IDEO CoLab Ventures.
-
Tier 4: P2P Capital, Zora.

Enso Team
-
Connor Howe (Founder & CEO): Strategic vision and leadership.
-
Milos Costantini (Co-Founder): Solidity development expert.
-
Peter Phillips (Co-Founder): Software engineering specialist.
Official Links
Also, you can freely share your thoughts and comments about the topic in the comment section. Additionally, please follow us on our Telegram, YouTube, and Twitter channels for the latest news and updates.