Hemi Network (HEMI) is a modular protocol that integrates Bitcoin and Ethereum, enhancing and expanding the core capabilities of these two leading blockchain networks. Let’s dive into what Hemi Network (HEMI) is and explore its functionality in detail.
What Is Hemi Network (HEMI)?
Hemi introduces an innovative approach to blockchain interoperability and scalability, treating Bitcoin and Ethereum as components of a unified supernetwork rather than separate ecosystems. This approach aims to:
-
Harmonize these leading networks into a secure, scalable, and resilient protocol.
-
Maximize the utility of the vast value stored across Bitcoin and Ethereum.
-
Provide a foundation for integrating the best features of blockchain technology with the broader internet.
At the core of the system lies the Hemi Virtual Machine (hVM), which encapsulates a full Bitcoin node within the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The Hemi Bitcoin Kit (hBK) makes hVM’s Bitcoin interoperability features accessible to developers. As a result, Hemi feels as familiar as an Ethereum Layer-2 network while fully leveraging Bitcoin’s capabilities. Applications that utilize Hemi’s Bitcoin awareness or dual-network asset system are called “hApps” to reflect their multi-chain capabilities.

Advantages of Hemi Network
Hemi’s approach delivers the following key benefits:
-
Proof-of-Proof (PoP) Superfinality: Transactions on Hemi achieve Bitcoin-level finality in just a few hours, maintaining sequencer decentralization without compromising Ethereum settlement speed.
-
Tunnels: Trustless and Trust-Minimized Cross-Chain Portability — The hVM provides protocol-level awareness of Bitcoin and Ethereum states, enabling secure cross-chain asset movement.
-
hVM and hBK: True Bitcoin DeFi — Hemi offers smart contracts highly granular, indexed views of Bitcoin state, enabling trustless DeFi applications and interoperability infrastructure previously unattainable on an EVM.
-
Chainbuilder: Instant Extensibility — External project teams can launch Hemi ecosystem chains (hChains) that leverage Hemi’s Bitcoin Security-as-a-Service (BSaaS) and dual-chain interoperability.
-
Encapsulation: On-Chain Asset Programmability — Hemi provides advanced asset-handling capabilities, such as on-chain routing, time-locks, and password protection.
Ultimately, Hemi not only creates an ideal platform for development on Bitcoin and Ethereum but also fosters a multi-chain interoperability ecosystem secured by Bitcoin.
Evaluation of Prior Approaches
Hemi Network combines Ethereum’s flexibility with Bitcoin’s security, expanding the capabilities and usability of both. Let’s briefly assess traditional approaches to scaling and integrating Bitcoin security.
Bitcoin Interoperability Approaches
-
BTC Relay: A smart contract system incentivizing third parties to relay Bitcoin headers to the protocol, validating PoW solutions and building a lightweight view of the canonical Bitcoin chain. However, it’s limited to verifying specific Bitcoin transactions and relies on external relayers.
-
BeL2: Uses zero-knowledge proofs to prove Bitcoin transaction existence, paired with a 2/3 multisig escrow system. It also depends on relayers and only confirms transaction inclusion in the canonical chain.
-
Chain-key ECDSA Bitcoin Integration: Block validators create a shared ECDSA key to manage Bitcoin wallets via smart contracts. Only UTXO data and Bitcoin fee levels are visible, limiting functionality.
Ethereum Scaling Approaches
-
Optimistic Rollups: Publishes transactions in batches to Layer-1, executing them off-chain and committing results to Layer-1. A seven-day challenge period causes delays and burdens users with fraud detection.
-
Zero-Knowledge (zk) Rollups: Bundles transactions and posts cryptographic proofs of correct execution to Layer-1. However, they often rely on centralized sequencers and opaque mempools.
-
Validiums: Only state roots are published to Layer-1, with the network responsible for data availability.
-
Sidechains: Independent blockchains connected to the main chain via a two-way bridge, with security dependent on the bridge.
Bitcoin Scaling Approaches
-
Federated Peg Sidechains: Use a federated or centralized bridge to move funds to a sidechain, adding features like Turing-complete smart contracts but requiring trust in bridge operators.
-
Drivechains (BIP 300): Employ a bridge governed by Bitcoin miners, who could collude to steal assets. Withdrawals can take three months.
-
Lightning: Creates state channels on Bitcoin, but malicious actors can lock funds for months, and advanced programmability is absent.

Bitcoin Security Inheritance Approaches
-
Merged Mining: Encourages Bitcoin miners to mine another chain in parallel, but miners can attack the new chain at no cost.
-
Blind Merged Mining (BIP 301): Offers a marketplace for sidechain block construction, but enables low-cost 51% attacks.
-
Meta-Protocol: Embeds new protocol transactions directly in the Bitcoin blockchain, limited by block size and fees.
-
Proof-of-Transfer (PoX): Miners send BTC to stakers for block mining, tightly coupling block production and security.
Hemi’s Proof-of-Proof (PoP) consensus mechanism improves on these approaches by:
-
Allowing Bitcoin miners to secure Hemi and earn fees without participating in Hemi’s consensus.
-
Scaling transaction throughput without increasing Bitcoin’s footprint.
-
Requiring a 51% attack on Bitcoin for deep reorganizations, which is economically infeasible.
-
Decoupling block production from Bitcoin security inheritance, maximizing decentralization and long-term incentive alignment.
Proof-of-Proof and Superfinality
Proof-of-Proof (PoP) is a complementary consensus protocol enabling Hemi Network to inherit Bitcoin’s full Proof-of-Work security in a decentralized, trustless, transparent, and permissionless manner. A lightweight miner type, Pop Miner, publishes Hemi consensus data to the Bitcoin blockchain, with successful miners rewarded in Hemi’s native token. Hemi uses these publications for fork resolution, preventing reorganizations with Bitcoin’s security. Hemi blocks achieve full Bitcoin finality in about 90 minutes (nine Bitcoin blocks), making reorganization mathematically impossible without a 51% attack on Bitcoin.
Decentralized Rollup Mechanics
Layer-2 chains periodically publish state roots to Layer-1 for asset bridging and cross-chain smart contract calls. In traditional Layer-2s, a centralized proposer pays Ethereum gas fees, but can halt the chain or enforce censorship. Hemi addresses this with decentralized Publisher and Challenger roles. Publishers post Hemi data to Ethereum and earn rewards, while Challengers detect invalid publications, slashing misbehaving Publishers’ stakes for rewards.
Asset Portability: Tunnels
Tunnels facilitate digital asset movement between Hemi, Bitcoin, and Ethereum. Hemi’s protocol-level awareness of Bitcoin and Ethereum states enables secure asset transfers beyond traditional bridges.
-
Bitcoin Tunnel: Offers centralized and decentralized custodianship for moving Bitcoin and Bitcoin-native assets to the EVM, using over-collateralized multisig for low-value assets and BitVM for high-value assets.
-
Ethereum Tunnel: Similar to optimistic rollups, but with faster settlement due to Bitcoin finality. Hemi-native assets can also be tunneled to Ethereum.
System Design Overview
Hemi Network’s architecture manages:
-
Decentralized Blockchain Progression: Deriving blocks from Ethereum, synchronizing Bitcoin block headers, calculating PoP payouts, and sequencing mempool transactions.
-
Bitcoin PoW Security Inheritance: Decentralized Hemi state publication to Bitcoin, fork resolution, and providing Bitcoin finality data.
-
EVM-Level Bitcoin Awareness via hVM: Advancing the Bitcoin view and exposing it to the EVM via precompile contracts.
-
Tunneling Ethereum and Hemi Assets: Processing deposits and withdrawals, validating faulty publications.
-
Tunneling Bitcoin Assets via hVM: Managing custodianship vaults, detecting deposits, coordinating withdrawals, and penalizing misbehavior.
Hemi Network (HEMI) Tokenomics
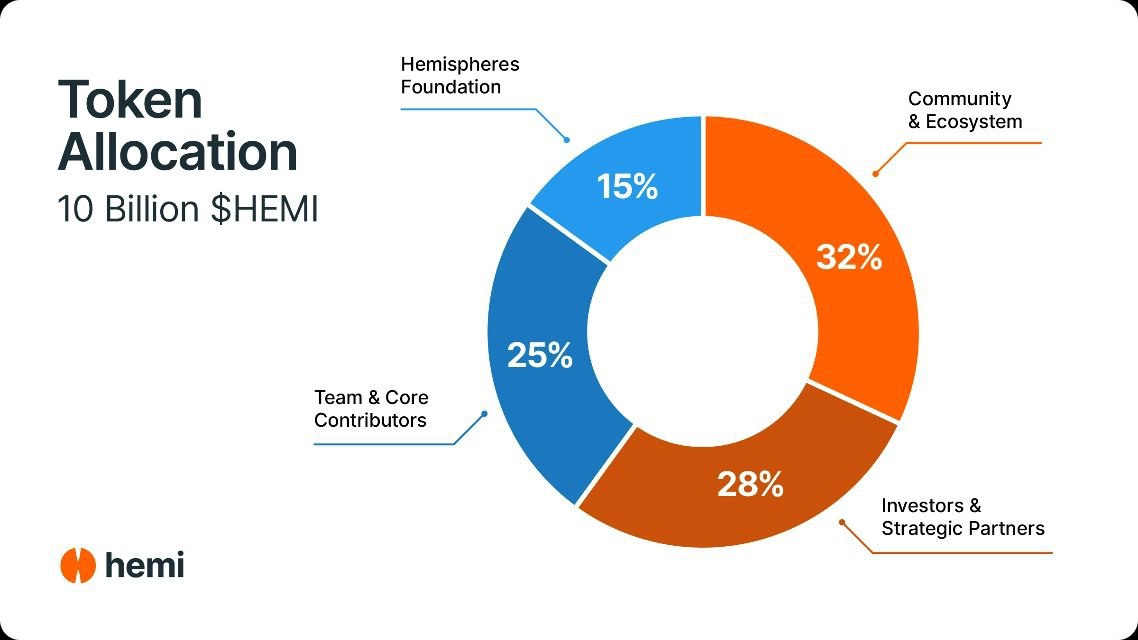
The HEMI token is the protocol’s native token with the following distribution:
-
Total Supply: 10 billion HEMI
-
Community and Ecosystem: 32%
-
Investors and Strategic Partners: 28%
-
Team and Core Contributors: 25%
-
Hemispheres Foundation: 15%
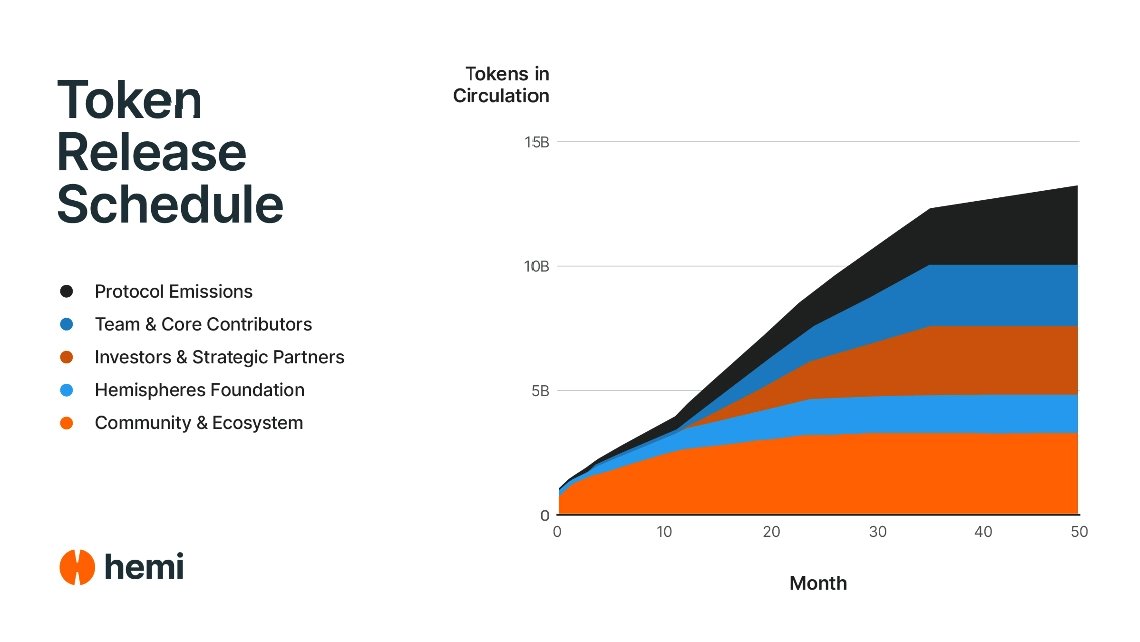
Hemi Vesting
Hemi Network (HEMI) Backers
Hemi Network is supported by prominent investors, including YZILabs, Breyer Capital, Big Brain Holdings, Crypto.com, and Gate.io. This robust backing strengthens Hemi’s innovative position in the DeFi ecosystem.

Hemi Network (HEMI) Team
Hemi Network is led by Jeff Garzik (Co-Founder) and Maxwell Sanchez (Co-Founder). This experienced team aims to create an innovative supernetwork uniting Bitcoin and Ethereum, making blockchain technology more accessible and powerful.

Official Links
You can also freely share your thoughts and comments about the topic in the comment section. Additionally, don’t forget to follow us on our Telegram, YouTube, and Twitter channels for the latest news and updates.


