Bitcoin (BTC), the popular cryptocurrency, is generated through a process known as mining. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems and are rewarded with Bitcoin for each successfully mined block. This process not only produces new Bitcoins but also facilitates transactions on the blockchain network.
You might also like: How To Use Binance Mobile Application? Detailed Binance Mobile Usage
One crucial aspect of the Bitcoin protocol is the halving system, which involves reducing the reward received per block by half. The halving events on Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain are scheduled to occur approximately every four years. The underlying principle is to gradually decrease the amount of new Bitcoin added to the network.
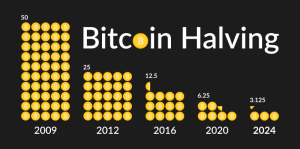
When Bitcoin first emerged in 2008, it provided a reward of 50 BTC per block. However, developers anticipated that as the number of miners increased and transaction speeds slowed down, adjustments were necessary. Therefore, they introduced the halving system and automatically reduced the reward per block.
The first halving took place in 2012, reducing the reward to 25 BTC per block. Another halving occurred in 2016, further reducing the reward to 12.5 BTC per block. In 2020, the reward was again halved to 6.25 BTC. This process will continue until the total supply of 21 million Bitcoins is mined, which is projected to happen around the year 2140.
Once all the Bitcoins have been mined, miners will face a significant change. They will no longer receive newly minted Bitcoins as direct income. Instead, they will rely on transaction fees within the network. This transition may result in a substantial increase in network fees, potentially leading to higher transaction costs.
You can present your own thoughts as comments about the topic. Moreover, you can follow us on Telegram and YouTube channels for this kind of news.


